Back to Kemp Acoustics Home



Next: List of Tables
Up: thesis
Previous: Contents
Contents
- Uniform pipe
- Detail of a waveguide consisting of straight sections of length
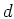 joined discontinuously
joined discontinuously
- Cylindrical waveguide with radius
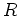
- Three dimensional plot of the Bessel function of the first kind of order 0 against radius on the
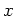 -
-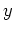 plane
plane
- The Bessel function of the first kind of order 0
- The modes in a cylindrical duct with
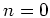 (plane wave mode),
(plane wave mode), 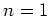 ,
, 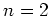 and
and 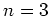 (evanescent). All have the same free space wavenumber
(evanescent). All have the same free space wavenumber
- Rectangular waveguide with halfwidths
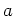 and
and 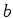
- Horn approximated by a series of cylinders
- Pressure field of a piston driven cylinder terminated in an infinite cylindrical pipe
- Piston in an infinite baffle
- Normalised direct radiation impedance of the
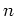 th mode in a circular duct of radius
th mode in a circular duct of radius 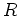 for
for 
- Coupled radiation impedances of a circular duct of radius R
- Geometry of infinitely flanged rectangular duct
- Radiation impedances of square and circular ducts
- Direct radiation impedances of square ducts
- Coupled radiation impedances of square ducts
- Effect of aspect ratio on radiation impedances of rectangular ducts
- Detail of a waveguide consisting of straight sections of length
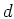 joined discontinuously
joined discontinuously
- Trumpet section input impedance
- Trumpet section input impedance
- Trumpet section input impedance
- Trumpet section pressure field: (a) plane wave approximation, (b) 2 modes, (c) 3 modes, (d) 5 modes, (e) 11 modes
- Trumpet section pressure field: 11 modes
- Travelling waves in a typical object split into cylindrical sections
- Schematic diagram of the apparatus
- The acoustic pulse reflectometer
- Object reflections
- Stepped tube connected to source tube
- Calibration pulse
- Input impulse response
- Stepped cylinder test object input impedance
- Trumpet section input impedance
- Stepped tube connected to source tube through dc tube
- Object reflections using dc tube
- Reconstruction of test object consisting of stepped cylinders
- Plane reflectance for a single discontinuity with
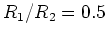
- Plane reflectance for a single discontinuity with
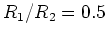 showing high frequency behaviour
showing high frequency behaviour
- Plane reflection spectrum for different discontinuity ratios against
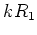
- Plane reflection spectrum for different discontinuity ratios against
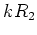
- Plane input impulse response calculated for a single discontinuity with
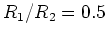
- Object reflections using virtual dc tube
- Reconstruction of test object consisting of stepped cylinders
- Calibration pulse including source reflections
- Reflections from long stepped cylinder test object including source reflections
- Second half of long stepped cylinder test object reflections
- Long stepped cylinder test object reflections
- French horn object reflections
- French horn bore reconstruction, first 3.5 metres
- French horn bore reconstruction, first 4.3 metres
- Feedback shift register and recurrence relation for
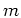 = 4
= 4
- Microphone signal for excitation with a
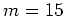 MLS signal repeated twice
MLS signal repeated twice
- Microphone signal chopped to show one period of response to continuous excitation with a
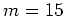 MLS signal
MLS signal
- System impulse response
- Calibration pulse isolated from system impulse response
- Object reflections isolated from system impulse response
- Reconstructions for different orders of MLS excitation
- Detail of a waveguide consisting of straight sections of length
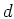 joined discontinuously
joined discontinuously
Jonathan Kemp
2003-03-24