| n |
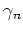 |
n |
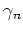 |
n |
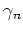 |
| 0 |
0.0000000 |
16 |
51.0435352 |
32 |
101.3126618 |
| 1 |
3.8317060 |
17 |
54.1855536 |
33 |
104.4543658 |
| 2 |
7.0155867 |
18 |
57.3275254 |
34 |
107.5960633 |
| 3 |
10.1734681 |
19 |
60.4694578 |
35 |
110.7377548 |
| 4 |
13.3236919 |
20 |
63.6113567 |
36 |
113.8794408 |
| 5 |
16.4706301 |
21 |
66.7532267 |
37 |
117.0211219 |
| 6 |
19.6158585 |
22 |
69.8950718 |
38 |
120.1627983 |
| 7 |
22.7600844 |
23 |
73.0368952 |
39 |
123.3044705 |
| 8 |
25.9036721 |
24 |
76.1786996 |
40 |
126.4460139 |
| 9 |
29.0468285 |
25 |
79.3204872 |
41 |
129.5878033 |
| 10 |
32.1896799 |
26 |
82.4622599 |
42 |
132.7294644 |
| 11 |
35.3323076 |
27 |
85.6040194 |
43 |
135.8711224 |
| 12 |
38.4747662 |
28 |
88.7457671 |
44 |
139.0127774 |
| 13 |
41.6170942 |
29 |
91.8875043 |
45 |
142.1544297 |
| 14 |
44.7593190 |
30 |
95.0292318 |
|
|
| 15 |
47.9014609 |
31 |
98.1709507 |
|
|
|